-
US$5 billion
targeted investment in new energy products and lower-carbon services by 2030
-
A$40 million
jointly invested in the Emerald Trade Monash Energy Partnership, which includes hydrogen research
-
3
hydrogen projects
Hydrogen – energy for a lower carbon future
Demand is growing for safe, clean, affordable and reliable energy that also helps the world decarbonise. Hydrogen can safely power everything petrol or gas can, without emitting CO². It’s clean, abundant, versatile, and can store energy at much higher densities than batteries. Best of all, when consumed, the only by-product is water. Hydrogen offers an exciting pathway for decarbonisation both domestically and for export. It is a huge commercial opportunity for Australia, with the potential to create thousands of new jobs and a multi-billion-dollar export market.

We look forward to H2Perth establishing Western Australia as a global hydrogen leader, building on our state’s existing resources and capabilities and helping lead us to into a lower-carbon future – something everyone can be proud of.
Meg O'Neill, Chief Executive Officer
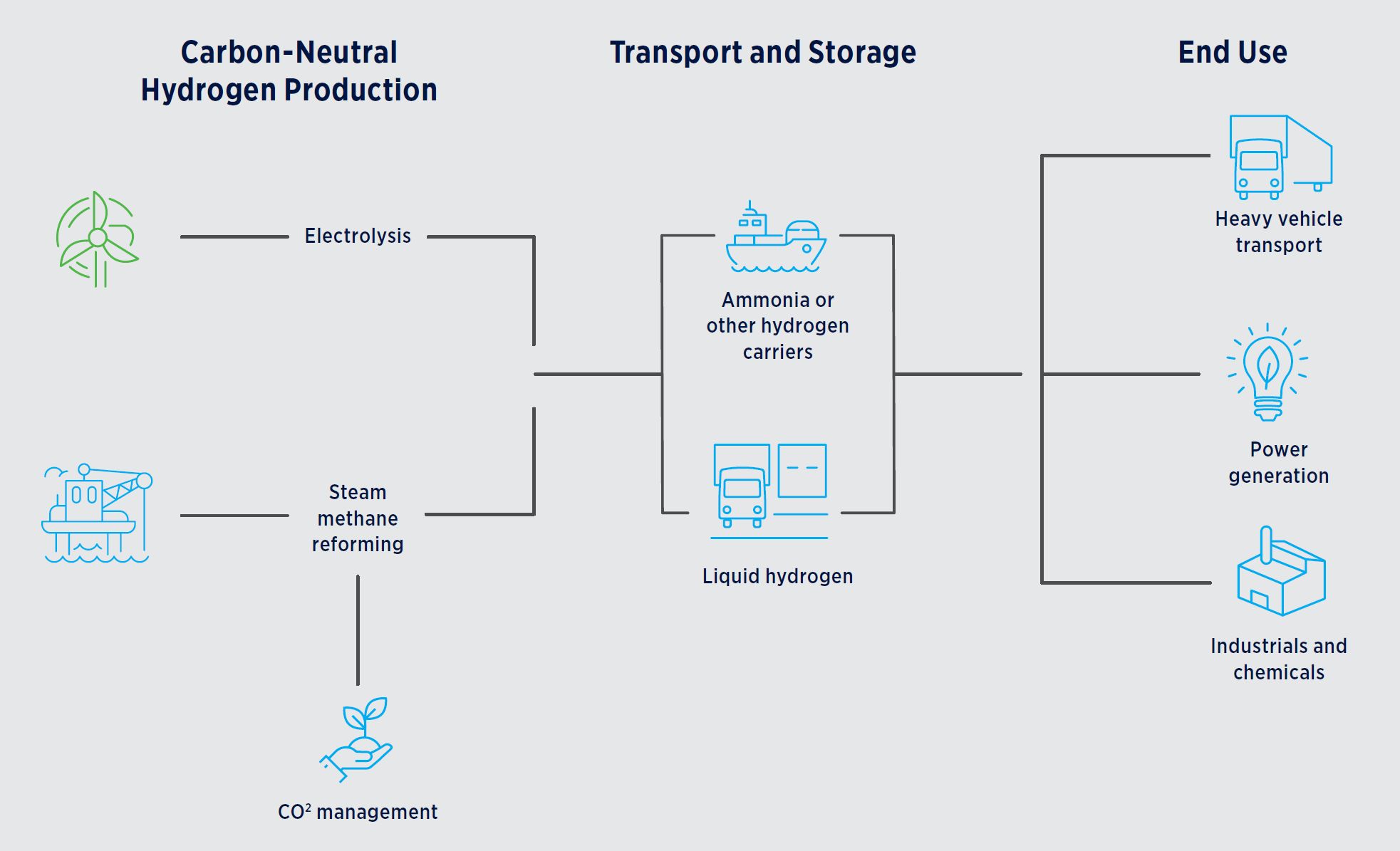
How can we make hydrogen?
We are developing new energy and low-carbon solutions - like hydrogen - that will be part of our future. Our principles for hydrogen development are: 1) customer led; 2) technology agnostic; and 3) lowest cost. We are looking at opportunities for both hydrogen from natural gas with process emissions abated, and hydrogen produced using renewable energy.
The majority of hydrogen available today is produced through a process called steam-methane reforming (SMR):
- Start with natural gas, which is largely made up of methane (containing four hydrogen atoms in each molecule).
- The gas is reacted with high-temperature steam to release the hydrogen.
- A small amount of carbon dioxide is generated during SMR, which we commit to managing through technical abatement or market offset.
Hydrogen can also be produced from renewable power sources, such as wind, solar, hydro, or geothermal.
- The renewable energy powers electrolysers, which split water into hydrogen and oxygen atoms.
- No carbon dioxide is produced.
- Currently, around 5% of the world's hydrogen is produced in this way. We want to see this share increase, but to get there, the hydrogen industry needs scale, driven by demand. This requires a competitive price.
Our hydrogen investment
We're working with partners in Australia and internationally to improve our understanding of the role hydrogen can play in global decarbonisation.
Thought leadership: the energy transition
We participated in a webinar series hosted by Monash University through the Emerald Trade Monash Energy Partnership. Our team spoke on different aspects of the energy transition: challenges and opportunities for renewable hydrogen, carbon reuse and energy transition.